
History of Superfluorescence
Albert Einstein Professor in Science at PU (1975-1984)
•Dicke Superradiance (1954)
https://journals.aps.org/pr/pdf/10.1103/PhysRev.93.99
Since then……
Bose- Einstein Condensates (1973)
•Plasmonics (Pustovit et al., Proc. SPIE 7757, Plasmonics: Metallic Nanostructures and Their Optical Properties VIII, 77571U (10 September 2010))
•Semiconductor Quantum Structures (G. Noe ll et al., Nature Physics 8, 219 (2012))
•Quantum Dot Superlattice (G. Raino et al., Nature 563, 671–675 (2018))
•Until recently, needs extremely low T (6K to 100K or high magnetic fields >10T) to suppress dephasing.
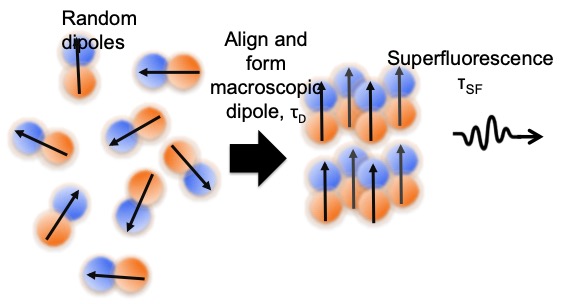
What is Superfluorescence?
•Short and intense burst of light.
•Pulse peak intensity scales as N2 and a lifetime that scales as tSF ~ tSP/N .
•Disrupted by phase relaxation.
No previous reports of Anti-Stokes shifted SF has been observed, at ambient temperature, and in a single nanocrystal until our breakthrough.

•4f orbitals of lanthanide (RE3+) ions shielded by the outer fully-occupied 5s and 5p.
•Each closely spaced RE3+ emitter interact with each other through the radiation field to establish coherence
•Anti-Stokes Superfluorescent Emission at Room Temperature
